Rich in history and flavor, mortadella is a prized Italian cold cut originating from Bologna in the Emilia-Romagna region. This delectable sausage boasts a distinctive appearance with its mosaic of heat-cured pork and glistening white fat cubes, each at least 15% of the meat’s composition. These tender cubes, primarily sourced from the pig’s throat, hold their shape during the slow-cooking process, ensuring a delightful textural contrast. Butchers traditionally season mortadella with black peppercorns, pistachios, and even myrtle berries, creating a unique flavor profile in each bite.
The name mortadella’s origins remain shrouded in some mystery. A popular theory suggests it stems from the Latin word “mortarium,” referencing the mortar and pestle used by the Romans to grind the meat and spices for this ancient sausage.
This report delves into the ingredients of a popular mortadella brand, dissecting each component’s role in the cold cut production process. By examining these ingredients, we gain a deeper understanding of how they contribute to the final product’s unique flavor, texture, and overall quality.
this Is a Beef mortadella wit olives
Ingredients of mortadella:
Beef Meat, Poultry Meat, Water, Olives, Soy Protein, Potato starch, Salt, Spices (wheat flour), Preservative (Sodium Lactate – E325), Sodium nitrite- E250, Fresh garlic, Emulsifier (carrageenan – E407), Sodium Tripolyphosphate – 450, Smoke flavor, Dextrose, Sugar, Antioxidant (sodium Ascorbate – E301),
calories in mortadella for 100g
| Amount per 100g | |
| Calories | 182 kCal |
| Total Fat | 12g |
| Saturated Fat | 3.3g |
| Trans Fat | 0g |
| Monounsaturated Fatty Acids | 5.8g |
| Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids | 1.6g |
| Cholesterol | 68mg |
| Total Carbohydrate | 6g |
| Dietary Fiber | 1.4g |
| Total sugars | — |
| Added sugar | — |
| Protein | 13g |
Beef meat processing:
Beef is the main ingredient in this product. Beef commonly consumed meats that can be processed in many different ways. The primary reason for processing beef is to improve consumer acceptability and convenience of preparation, and to extend shelf life. To achieve this, processing usually accomplishes the following. (2)
- 1. Remove bones.
- 2. Make connective tissue less objectionable, by removal of extremely tough or inedible pieces.
- 3. Ensure the fat to lean ratio is appropriate.
Poultry Meat:
Poultry is added to meat mortadella even though it is not mentioned at the front label. It is added manly to reduce product cost as will as the following (3)
- Cost Reduction: MSC is cheaper than beef, allowing for lower mortadella prices.
- Fat Control: Poultry can help lower the overall fat content, especially in low-fat mortadella recipes.
- Good Consistency: MSC contributes to a good product consistency at a low cost.
MSC:
Mechanically separated poultry (chicken or turkey) is a low-cost poultry protein, which is produced by mechanically separating bone and attached skeletal muscle .(4)
Water in mortadella
Water in mortadella processing for two main reasons:
- Ingredient Functionality: Water helps disperse dry ingredients and proteins, dissolves or suspends other ingredients like phosphates and salt, and plays a role in extracting protein during mixing. This contributes to the overall product consistency. (5)
- Temperature Control: Grinding and mixing generate heat, which can negatively affect the mortadella. Water, especially cold water or ice, helps maintain a cool temperature. This prevents fat smearing, broken emulsions (separation of ingredients), and promotes microbial safety by reducing bacterial growth. Additionally, colder temperatures or Ice allow for longer mixing times, further improving protein extraction and consistency. (6)
Soy protein in mortadella
- Enhanced Textural Properties and Binding: Soy protein functions as a binder, promoting improved cohesion between meat particles and ultimately resulting in a firmer final product.
- Yield Improvement and Cost Optimization: The addition of soy protein allows for product extension, enabling manufacturers to produce a greater quantity of cold cuts or mortadella while utilizing the same amount of meat, thereby enhancing cost-efficiency.
- Moisture Retention: Soy protein possesses water-binding properties, contributing to improved product juiciness and minimizing drying out during storage.
- Seasoning effect in meat products: soy protein contains a small quantity of fatty acids and carbohydrates that generate a characteristic savory note upon heating. This unique bean aroma can effectively mask any off-odors present in the meat.
- Other Functional Properties: The text also mentions soy protein’s ability to create foams, improve stickiness (adhesion), and form gels, although their specific applications in mortadella are not elaborated on. (8)
Potato starch
- Improved Water Binding: Modified starch, compared to regular starch, might have a higher phosphate content which leads to larger starch granules and better gelatinization (absorption of water). This translates to increased water-holding capacity in the final product, reducing cooking and reheating losses.
- Fat Reduction: Modified starch can act as a fat replacer, allowing manufacturers to reduce fat content in sausages while maintaining a desirable texture.(9)
- Emulsion Binding: Modified starch can contribute to binding emulsions, which is essential for maintaining a stable and uniform product structure.(10)
Salt
- Flavor Enhancement: Salt contributes its own taste profile to meat and also intensifies the flavors of other spices used in the recipe.
- Improved Water Retention: Salt plays a crucial role in retaining moisture within the meat. It achieves this by:
- Solubilizing Proteins: Salt helps dissolve meat proteins, which can then bind more water molecules.
- Affecting pH: Salt alters the meat’s pH level, bringing it closer to its isoelectric point (pI) ph 4.8 rather than 5.2. At this pI, meat proteins have minimal charge and attract more water molecules, enhancing water-holding capacity.
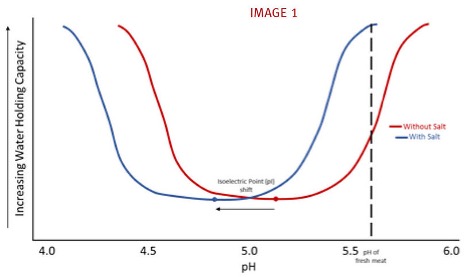
salt (NaCl) on microbial communities within meat products. The addition of salt alters the environmental conditions, exerting a selective pressure on various bacterial populations.
- Growth Inhibition: Salt generally creates a hostile environment for many bacteria, leading to either a reduction in growth rate or complete cell death. This phenomenon is referred to as a “microbial inversion.”
- Selective Effect: Different bacterial species exhibit varying degrees of salt tolerance. Common foodborne pathogens such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., and Campylobacter jejuni are particularly susceptible to salt and struggle to thrive in high-salt environments.(15)
Spices (wheat flour)
Enhance flavor, gelatinization
Preservative (Sodium Lactate – E325)
Sodium lactate (E270) is a naturally occurring organic acid derived from lactic acid. Lactic acid is produced by bacterial fermentation, a process widely employed in the production of fermented foods such as yogurt and sauerkraut. The human large intestine also harbors bacterial populations that contribute to lactic acid production.
Commercially, sodium lactate is manufactured through the bacterial fermentation of starch and molasses. This process leverages the natural metabolic capabilities of bacteria to produce a valuable food additive.
Functional Properties of Sodium Lactate
- Antimicrobial Activity: Sodium lactate exhibits antimicrobial properties, particularly against yeasts and fungi. This characteristic makes it a valuable preservative in food applications, helping to extend shelf life and prevent spoilage.
- Antioxidant Synergy: Sodium lactate can enhance the stability of antioxidants when used in combination. This offers an additional layer of protection against oxidative damage in food products.
- Moisture Retention: Sodium lactate possesses moisture-retaining properties, which can be beneficial in preventing product drying during storage.
Safety Considerations:
sodium lactate metabolism may be limited in infants and young children. Their developing digestive systems might lack the necessary enzymes for efficient lactate processing. (13)
Sodium nitrite- E250
Sodium nitrite is a naturally occurring mineral, but it can also be produced from the food additive sodium nitrate
Functions in Meat Products:
- Preservative: It protects against Clostridium botulinum, a dangerous bacteria that causes botulism.
- Color Fixative: Sodium nitrite helps maintain the desired red color in cured meats.
Safety Concerns:
- Nitrosamine Formation: Nitrites can react with protein in the stomach to form potentially carcinogenic nitrosamines.
- Hemoglobin Interference: High concentrations can affect hemoglobin function, especially in infants with a different type of hemoglobin.
- Poisoning Risk: Improper use during processing can lead to serious poisoning.(11)
Emulsifier (carrageenan – E407)
Carrageenan is a natural ingredient derived from red seaweed. Harvested from the ocean, it finds a variety of uses in food production. It acts as a gelling agent, thickener, and stabilizer, contributing to the texture of various products like meat, jellies, ice creams, and puddings. In Europe, it’s identified by the food additive numbers E407 (for carrageenan itself) and E407a (for carrageenan with added cellulose). Generally considered safe, carrageenan is also vegan, halal, kosher, and gluten-free.
Semi Refined (left) and Refined (right) kappa Powder
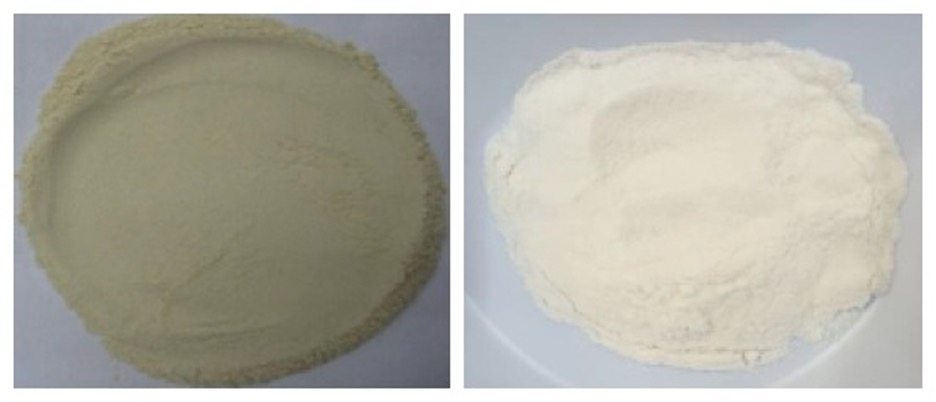

Semi Refined (left) and Refined (right) kappa Gel
the advantages of using kappa carrageenan in meat products:
- Improved Processing: Kappa carrageenan’s high brine gel strength and fine particle size make it suitable for tumbling or injecting meat during processing.
- Enhanced Texture and Yield: It functions as a thickener, binder, and stabilizer, contributing to a better texture in the final product. This includes improved moisture retention, increased weight yield, and superior slicing ability.
- Functional Benefits: Kappa carrageenan offers several desirable properties for meat products:
- Excellent water holding capacity, leading to a juicier and more flavorful product.
- Softer texture and a more uniform consistency.
- Stabilization of fat-protein emulsions for a smooth texture.
- Enhanced slicing ability and mouthfeel.
- Increased freeze-thaw stability, which is important for frozen meat products.
- Contribution to a softer texture with improved tenderness and juiciness.
Sodium Tripolyphosphate – 450
Multifunctional Additive in Processed Meat
- Applications: STP is a versatile food additive (E450) used to enhance texture, promote stability, and act as an emulsifier in various food processing applications. While it has some industrial uses, environmental concerns are leading to its replacement in some areas.
- Functions in Meat Products: Similar to salt and nitrite, STP plays several key roles in processed meats:
- pH Modification: It acts as an alkaline agent, raising the meat’s pH. This, along with protein interactions, improves water holding capacity. The text includes a graph illustrating this pH increase and its impact on water retention.
- Protein Solubilization: Like salt, STP affects muscle proteins (actin and myosin). It helps break down protein cross-bridges formed during rigor mortis, causing proteins to swell and hold more water, fat, and other proteins within the meat.
- Improved Water Holding Capacity: By increasing the pH and promoting protein solubilization, STP enhances the meat’s ability to retain water. This translates to higher product yield by minimizing water loss during cooking and storage.
- Sensory Properties: The text mentions that STP may also influence sensory properties like flavor, texture, and color in processed meats, but doesn’t elaborate on the specifics.
- Stabilizer: Prevents separation of ingredients and maintains texture.
- Thickener: Increases the viscosity of food products.(16)
Smoke flavor in mortadella
Smoke flavoring solutions (Pyroligneous extract) can be directly incorporated as an ingredient during product formulation. This method offers versatility and is used in various food products beyond meats, including sausages, cheese spreads, barbecue sauces, soups, and even snack foods.
Smoke flavoring solutions can be directly incorporated as an ingredient during product formulation. This method offers versatility and is used in various food products beyond meats, including sausages, cheese spreads, barbecue sauces, soups, and even snack foods.(17)
Sugar in mortadella:
Sugar plays a multifaceted role in food formulation, contributing to both flavor development and textural properties.
- Sugar as a flavor enhancer: helps to balance the flavor and make them more palatable, Sugar can mask undesirable flavors and enhance others
- Reduce saltiness of food: Sugar can also counteract saltiness, especially if you’ve over seasoned your dish
- Sugar as an anticoagulant: when it’s heated, sugar delays the coagulation of proteins (or the change to a more semi-solid state), which is useful for products such as baked custards and other desserts.
- Maillard Reaction: Sugar interacts with proteins during the Maillard reaction, a process responsible for the development of desirable brown color and caramelized flavors in cooked foods.(1)
Antioxidant (sodium Ascorbate – E301) in mortadella
- Sodium ascorbate is a mineral salt derived from vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Its molecular formula is C6H7NaO6.
- It provides some sodium. For every 1,000 mg of ascorbic acid in sodium ascorbate, there are approximately 131 mg of sodium.
- Food Additive Applications (E301):
- Antioxidant: It helps prevent spoilage by protecting against oxidation.
- Acidity Regulator: It can be used to control the acidity of food products.



